
Factory overheads cannot be conveniently allocated to cost units, which gives rise to the apportioning problem.
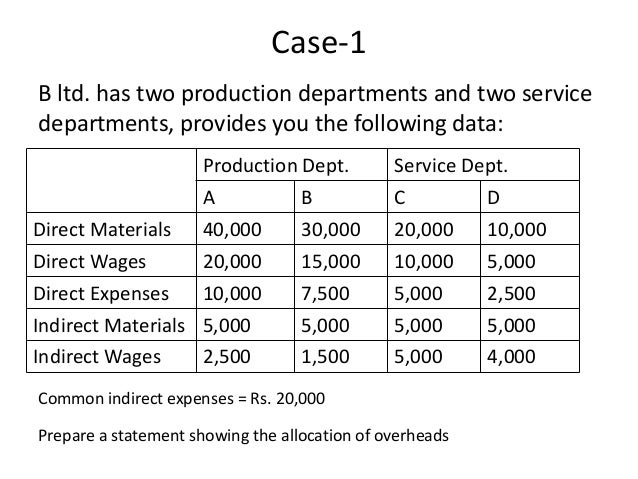
Several problems associated with factory overheads are stated as follows: Absorption of expenses of each department over the job, process, or product completed during the period in the department concerned.Re-appropriation of expenses related to service departments so as to include them in the production cost.Appropriation of expenses to the production unit(s) and service departments that cannot be conveniently allocated.Allocation of expenses to service departments.Since overheads cannot be allocated to cost units directly, the following steps are necessary for its proper accounting: Steps Needed for Proper Accounting of Factory Overheads Consumable stores and all forms of indirect material (i.e., material that cannot be traced as part of the finished product, such as oils and greases, small tools, cleaning materials, and minor spare parts for repairs).Wages and salaries (other than direct labor) of persons engaged in the factory (e.g., foremen, supervisors, maintenance staff, factory administrative or clerical staff, testers, and examiners).Depreciation of factory plant and machinery and buildings.Factory maintenance (e.g., cleaning, servicing, repairs, oiling, and greasing).Factory expenses (e.g., rent, rates, insurance, water, heat, and electricity).Examples of Factory OverheadsĮxamples of items included in factory overheads include: These are also referred to as production overheads or works overheads. The factory overhead is the total of all costs (other than direct costs) incurred to maintain and run the production facility or factory. Such expenditures are known as factory overheads. These expenditures cannot be allocated to a particular job, process, or item of production. The main cost of a product consists of direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses.īesides these expenses, there are certain indirect expenditures that cannot be conveniently identified with the article produced.
Overheads are an element of cost but they are a supplementary cost and cannot be directly added to a particular job. Instead, they are apportioned across the cost units on an equitable basis. The benefits arising from these costs cannot be associated with a specific cost unit. Factory overheads are the aggregate of indirect materials, labor, and other costs that cannot be identified conveniently with the articles produced or services rendered.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
